?? vs || Operator in Javascript
Jan 16, 2023
2 minutes
There are two operators ?? (Nullish coalescing operator) and || (OR Operator) which is confusing though their usage is almost similar but there is a subtle difference between the two which we will be going through in this post.
The Difference
The important difference between them is that:
|| returns the first truthy value
?? returns the first defined value
The result of a || b is:
- if the Boolean type conversion value of a is true i.e Boolean(a)=true, then a,
- if the Boolean type conversion value of b is false i.e Boolean(a)=false, then b,
The result of a ?? b is:
- if a is defined, then a,
- if a isn’t defined, then b.
What does that mean?
Let’s see this through different examples:
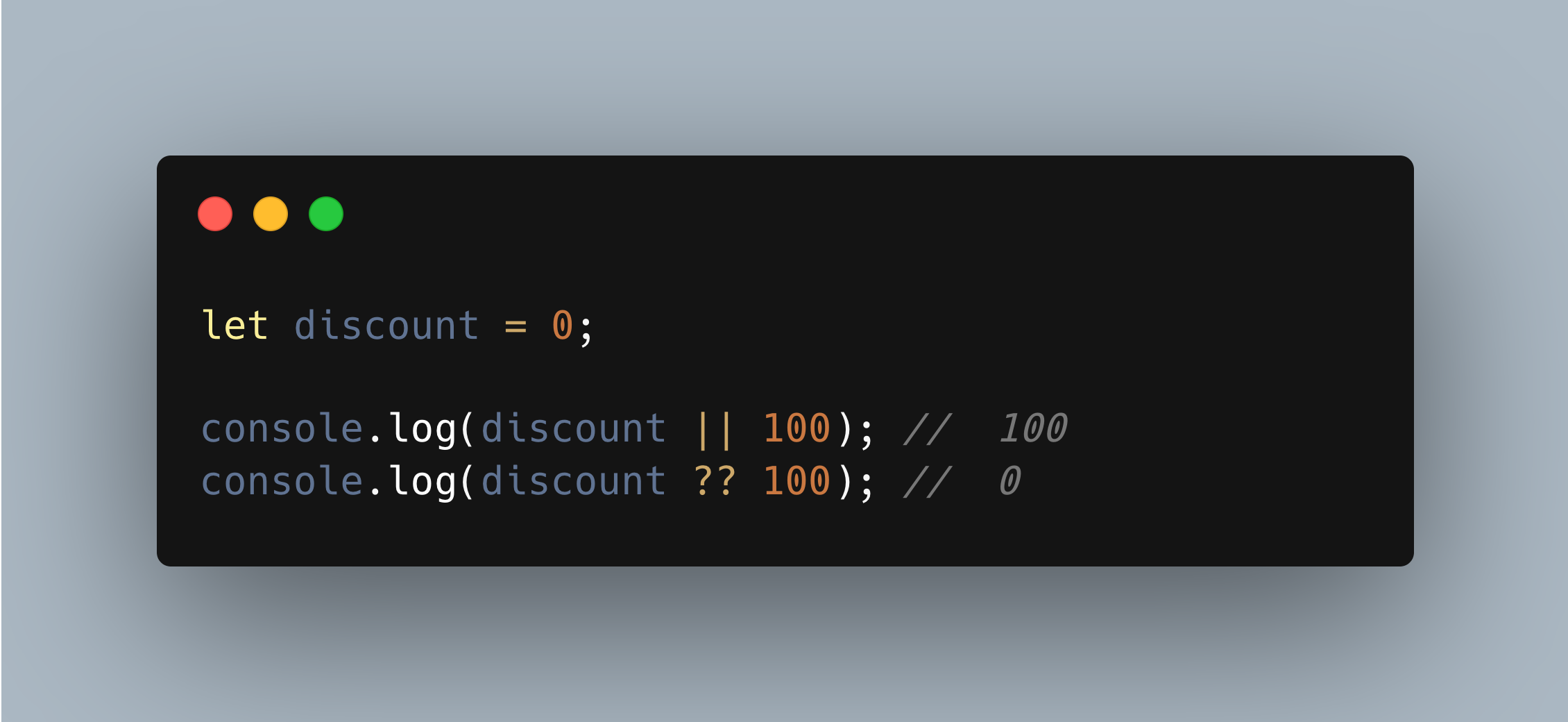
Example 1
let discount = 0;
console.log(discount || 100); // 100
console.log(discount ?? 100); // 0
Here, the discount is 0 so
||will result to 100 sinceBoolean(0) = false??will result in 0 because 0 is defined
Example 2
let discount = 1;
console.log(discount || 100); // 1
console.log(discount ?? 100); // 1
Here, the discount is 1 so
||will result to 1 sinceBoolean(1) = true??will result in 1 because 1 is defined
Example 3
let discount = null;
console.log(discount || 100); // 100
console.log(discount ?? 100); // 100
Here, the discount is null so
||will result in 100 because it evaluates null as false sinceBoolean(null) = false??will result in 100 because null is undefined
Example 4
let discount = "";
console.log(discount || 100); // 100
console.log(discount ?? 100); // ""
Here, the discount is an empty string so
||will result in 100 because it evaluates an empty string as false sinceBoolean("") = false??will result in “” because an empty string is defined in JS
Using ?? with && or ||
Javascript forbids using with ??, || and && together. It will raise Syntax Error.
let x = 1 || 2 ?? 3; // Syntax error
However you can use explicit parentheses to work around it:
let x = (1 || 2) ?? 3; // 1
Conclusion
- The nullish coalescing operator ?? provides a short way to choose the first “defined” value from a list.
- It’s used to assign default values to variables:
discount = discount ?? 10 // assigns discount as 10 if its null/undefined
- The OR operator || provides a short way to choose the first truthy value from a list.
- You cannot use operators
??with&&or||together. You need to use explicit parantheses
